Students can download solutions for JEE Advanced 2020 question paper 2 for Chemistry subject from this page. The questions have been solved in a detailed manner by subject experts at BYJU'S. Practising these questions will help the JEE aspirants to understand the overall exam pattern and prepare accordingly for upcoming exams. To score a higher rank in the JEE Advanced exams students are advised to practice previous years' papers.
Paper 1 - Chemistry
Question 1: The 1st, 2nd, and the 3rd ionization enthalpies, ?1, ?2, and ?3, of four atoms with atomic numbers n, ? + 1, ? + 2, and ? + 3, where ? < 10, are tabulated below. What is the value of n?
|
Atomic Number |
Ionization Enthalpy (kJ/mol) |
||
|
I1 |
I2 |
I3 |
|
|
n |
1681 |
3374 |
6050 |
|
n+1 |
2081 |
3952 |
6122 |
|
n+2 |
469 |
4562 |
6910 |
|
n+3 |
738 |
1451 |
7733 |
Solution:
Answer: 9
According to the tabulated data,
Element with Atomic number (n+2), should be an alkali metal
As we see, first ionization enthalpy (I1) is very less but second ionization enthalpy (I2) is very large.
Hence, atomic number can be = 11
That is, (n + 2) = 11
n = 9
Note: 'n' can't be '1'.
Question 2: Consider the following compounds in the liquid form:
O2, HF, H2O, NH3, H2O2, CCl4, CHCl3, C6H6, C6H5Cl.
When a charged comb is brought near their flowing stream, how many of them show deflection as per the following figure?

Solution:
Answer: 6
Only polar molecules are deflected by charged comb.
Polar molecules: HF, H2O, NH3, H2O2, CHCl3, C6H5Cl
Non-polar molecules: O2, CCl4, Benzene
Question 3: In the chemical reaction between stoichiometric quantities of KMnO4 and KI in weakly basic solution, what is the number of moles of I2 released for 4 moles of KMnO4 consumed?
Solution:
Answer: 6
Chemical reaction of KMnO4 and KI in weakly basic solution is given as

Equivalents of KMnO4= Equivalents of I2
n-factor × Number of moles (n) = n-factor × Number of moles (n)
3 × moles of KMnO4 = 2 × moles of I2
3 × 4 = 2 × moles of I2
Moles of I2 = 6 moles
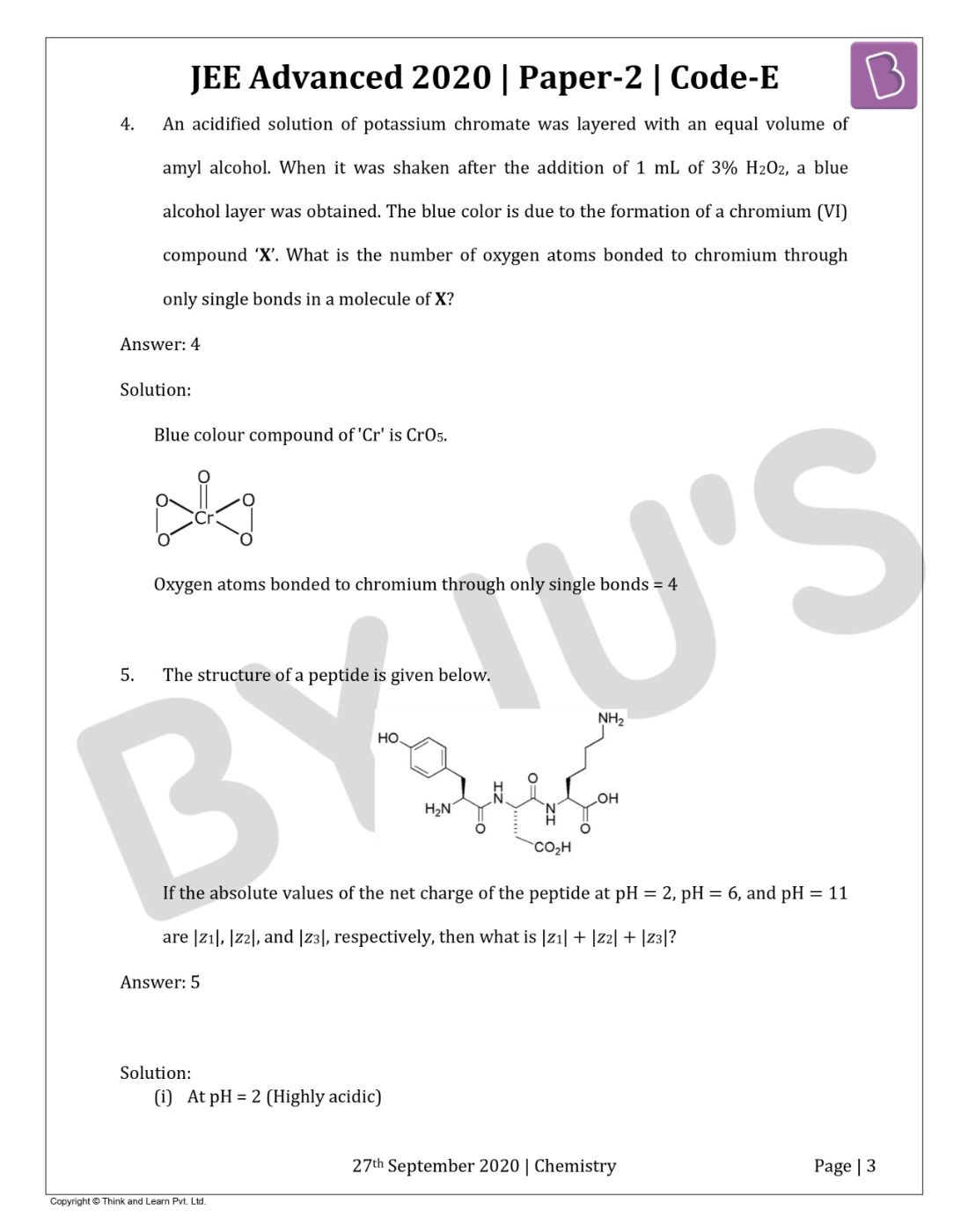
Question 4: An acidified solution of potassium chromate was layered with an equal volume of amyl alcohol. When it was shaken after the addition of 1 mL of 3% H2O2, a blue alcohol layer was obtained. The blue color is due to the formation of a chromium (VI) compound ‘X’. What is the number of oxygen atoms bonded to chromium through only single bonds in a molecule of X?
Solution:
Answer: 4
Blue colour compound of 'Cr' is CrO5.

Oxygen atoms bonded to chromium through only single bonds = 4
Question 5: The structure of a peptide is given below.

If the absolute values of the net charge of the peptide at pH = 2, pH = 6, and pH = 11 are |?1|, |?2|, and |?3|, respectively, then what is |?1| + |?2| + |?3|?
Solution:
Answer: 5
(i) At pH = 2 (Highly acidic)
In highly acidic medium, the given tripeptide exists as cationic form.

Net charge +2
|Z1| = 2 at pH = 2
(ii)At pH = 6 (neutral solution)
In neutral medium, the given tripeptide exists as Zwitter ion.

net charge = 0
|Z2| = 0 at pH = 6
(iii)At pH = 11 (basic medium)
In basic medium the given tripeptide exists in anionic form.

Net charge = –3
|Z3| = 3
Therefore, |Z1| + |Z2| + |Z3| = 2 + 0 + 3 = 5
Question 6: An organic compound (C8H10O2) rotates plane-polarized light. It produces pink color with neutral FeCl3 solution. What is the total number of all the possible isomers for this compound?
Solution:
Answer: 6
DBE (Double bond equivalent) of C8H10O2 is
= Number of carbon atoms – (Number of monovalent atoms)/2 + 1
= 8 – 10/2 + 1 = 4
It gives pink colour with neutral FeCl3 solution. It means phenolic group should be present in the compound.
Note: C* represent chiral carbon. So it will have (d and l) optically active isomers.

Total optically active isomer = 6
Question 7: In an experiment, m grams of a compound X (gas/liquid/solid) taken in a container is loaded in a balance as shown in figure I below. In the presence of a magnetic field, the pan with X is either deflected upwards (figure II), or deflected downwards (figure III), depending on the compound X. Identify the correct statement(s).

- a) If X is H2O(l), deflection of the panis upwards.
- b) If X is K4[Fe(CN)6](?), deflection of the panis upwards.
- c) If X is O2 (?), deflection of the panis downwards.
- d) If X is C6H6(l), deflection of the panis downwards.
- a) x = H2O → Diamagnetic
b) x = K4[Fe(CN)6] → Diamagnetic
Here, Fe+2 strong field ligand.
→ 3d6 ⇒ [t2g6, eg0]
c) x = O2 → ParamagneticHere, O2(g) is paramagnetic due to two unpaired electrons present in pi* (antibonding orbitals)
d) x = C6H6 (l) → diamagnetic (incorrect)It is due to presence of 0 unpaired electrons.
Solution:
Answer: A, B, C
Paramagnetic substances are attracted by magnetic fields & diamagnetic substances are repelled by magnetic field.
O2 - is paramagnetic
H2O & C6H6(l) - are Diamagnetic
& K4[Fe(CN)6] is also Diamagnetic
a) x = H2O → Diamagnetic b) x = K4[Fe(CN)6] → DiamagneticHere, Fe+2 strong field ligand.
→ 3d6 ⇒ [t2g6, eg0]
c) x = O2 → ParamagneticHere, O2(g) is paramagnetic due to two unpaired electrons present in pi* (antibonding orbitals)
d) x = C6H6 (l) → diamagnetic (incorrect)It is due to presence of 0 unpaired electrons.
Question 8: Which of the following plots is (are) correct for the given reaction?
([P]0 is the initial concentration of P)

- c) x = a{1 – e–kt}
x/a = 1 – e–kt
x/a = Q/P0

Solution:
Answer: A

As there is no inversion. Hence should be
SN1 → 1st order
c) x = a{1 – e–kt}
x/a = 1 – e–kt
x/a = Q/P0

Question 9: Which among the following statement(s) is(are) true for the extraction of aluminium from bauxite?
- a) Hydrated Al2O3 precipitates, when CO2 is bubbled through a solution of sodium aluminate.
- b) Addition of Na3AlF6 lowers the melting point of alumina.
- c) CO2 is evolved at the anode during electrolysis.
- d) The cathode is a steel vessel with a lining of carbon.
Solution:
Answer: A, B, C, D
Refer topic metallurgy
Refer topic metallurgya)Extraction of aluminium (Hall's process and Hall Heroult's electrolytic cell):
The process involved in extraction of aluminium is Hall Heroult’s process.
During process, Al2O3 is obtained as precipitate.
When CO3 is bubbled through a solution of sodium aluminate.
The reaction is given as:
2Na[Al(OH)4](aq.) + CO2 → Na2CO3 + H2O + 2Al(OH)3 (↓) or Al2O3.2H2O (ppt)
Refer topic metallurgyb) Electrolytic reduction of pure alumina takes place in steel box with lining of carbon (cathode) with cryolite (Na3AlF6) and fluorspar (CaF2) which lowers the melting point and increases the conductivity of electrolyte.
Refer topic metallurgyc) Electrolysis process in Hall’s process:
Graphite rods acts as anode:
At cathode:
Al+3 + 3e– → Al
At anode: The oxygen liberated at anode reacts with the carbon of anode to produce CO and CO2.
C + O2– → CO + 2e–
C + 2O2– → CO2 + 4e–
Refer topic metallurgyd)Here the cathode is a steel vessel with a lining of carbon.
Question 10: Choose the correct statement(s) among the following.
- a) SnCl2.2H2O is a reducing agent.
- b) SnO2 reacts with KOH to form K2[Sn(OH)6].
- c) A solution of PbCl2 in HCl contains Pb2+and Cl−ions.
- d) The reaction of Pb3O4 with hot dilute nitric acid to give PbO2 is a redox reaction.
Solution:
Answer: A, B
a)SnCl2.2H2O is a reducing agent since Sn2+ tends to convert into Sn4+
SnO2 + KOH → K2SnO3 + H2O
or
Amphoteric K2[Sn(OH)6]
b)First group cations (Pb2+) form insoluble chloride with HCl that is PbCl2 however it is slightly soluble in water and therefore lead +2 ion is never completely precipitated on adding hydrochloric acid in test sample of Pb2+, rest of the Pb2+ ions are quantitatively precipitated with H2S in acidic medium.
So that we can say that filtrate of first group contain solution of PbCl2 in HCl which contains Pb2+and Cl–.
However, in the presence of conc. HCl or excess HCl it can produce H2[PbCl4].
So, we can conclude A, B or A,B,C should be answers
PbCl2 + HCl → H2 [PbCl4]
Pb3O4 + HNO3 → PbO2 + Pb(NO3)2 + H2O
or
2PbO.PbO2 (Non redox reaction)
Question 11: Consider the following four compounds I, II, III, and IV.

Choose the correct statement(s).
- a) The order of basicity is II >I >III >IV.
- b) The magnitude of pKb difference between I and II is more than that between III and IV.
- c) Resonance effect is more in III than in IV.
- d) Steric effect makes compound IV more basic than III.
- a)Correct basic strength order of given compound is
(IV) > (II) > (I) > (III)
b) Compound IV is a stronger base than III due to SIR effect, which basic strength difference between I & II is very less.
c) In compound IV due to SIR (steric inhibition due to resonance) effect both –NO2 and N(CH3)2 group will be out of plane hence resonance effect in compound IV is less.
Solution:
Answer: C, D
a)Correct basic strength order of given compound is(IV) > (II) > (I) > (III)
b) Compound IV is a stronger base than III due to SIR effect, which basic strength difference between I & II is very less.
c) In compound IV due to SIR (steric inhibition due to resonance) effect both –NO2 and N(CH3)2 group will be out of plane hence resonance effect in compound IV is less.
Question 12: Consider the following transformations of a compound P.

Solution:
Answer: B, C

• NaNH2 acts as a base for the double elimination of geminal or vicinal dihalides to give alkynes.
• Pd-C / quinoline + H2 ⇒ a lindlar’s catalyst that reduce only alkynes not alkenes.
Question 13: A solution of 0.1 M weak base (B) is titrated with 0.1 M of a strong acid (HA). The variation of pH of the solution with the volume of HA added is shown in the figure below. What is the p?b of the base? The neutralization reaction is given by
B + HA → BH+ + A−.

Solution:
Answer: 3.3


kb = 5 × 10–4
pkb = –logkb = –log(5 × 10–4) = –log5 + 4log10
pkb= 4 – 0.7
pkb= 3.3
Question 14: Liquids A and B form ideal solution for all compositions of A and B at 25℃. Two such solutions with 0.25 and 0.50 mole fractions of A have the total vapor pressures of 0.3 and 0.4 bar, respectively. What is the vapor pressure of pure liquid B in bar?
Solution:
Answer: 0.2
PTotal = 0.3, where xA =
xA + xB = 1
⇒ xB = 0.75 =
⇒ 0.3= + …(1)
PTotal = 0.4 where xA=, xB =
⇒ 0.4= + .…(2)
Apply eq.(1) × 2 – eq.(2), we get
= 0.2 bar
Question 15: The figure below is the plot of potential energy versus internuclear distance (?) of H2 molecule in the electronic ground state. What is the value of the net potential energy ?0 (as indicated in the figure) in kJ mol−1, for ? = ?0 at which the electron-electron repulsion and the nucleus-nucleus repulsion energies are absent? As reference, the potential energy of H atom is taken as zero when its electron and the nucleus are infinitely far apart.
Use Avogadro constant as 6.023 × 1023 mol−1.

Solution:
Answer: –5242.42
P. E of 2 H-atoms
Total eng = P.E./2
Potential Energy = 2 Total Energy
E = -13.6 x z2/n2 ev/atom
= –2 x 13.6 x z2/n2 ev/atom + (–2 x 13.6 x z2/n2) ev/ atom
= – 2x 2 x 13.6 x 1 x ev/atom
= – 4 x 13.6 x 1.6 x 10–19 J/atom × 6.023 × 1023 atom/mole
= – 4 × 13.6 × 1.6 × 6.023×104 J/mole
= – 5242.42 KJ/mol
Question 16: Consider the reaction sequence from P to Q shown below. The overall yield of the major product Q from P is 75%. What is the amount in grams of Q obtained from 9.3 mL of P? (Use density of P = 1.00 g mL−1; Molar mass of C = 12.0, H =1.0, O =16.0 and N = 14.0 g mol−1)

Solution:
Answer: 18.6

Molecular weight of aniline (C6H5NH2) = 77 + 14 + 2 = 93
Density of P = 1 gm ml–1
d = m/v
or m = dv
Mass of P = 9.3 × 1 = 9.3 g
9.3 ml of P = 9.3 gm
P = of P

= 1:1:1
So,the mole of Q formed will be 0.1 mole and extent of reaction is 100% but if it is 75% yield.
Then amount of Q = 0.1 x 75/100 = 0.075 mol
The molecular formula of Q = C16H12ON2
So, M. wt. of Q = 16 x 12 + 12 x 1 + 16 + 2 x 14
= 192 + 12 + 16 + 28
= 248 gm / mol
So, amount of Q = 248 x 0.075= 18.6 gm
Question 17: Tin is obtained from cassiterite by reduction with coke. Use the data given below to determine the minimum temperature (in K) at which the reduction of cassiterite by coke would take place.
At 298 K: ∆??0(SnO2(?)) = −581.0 kJ mol−1, ∆??0(CO2(g)) = −394.0 kJ mol−1,
?0(SnO2(s)) = 56.0J K−1mol−1, ?0(Sn(s)) = 52.0 J K−1mol−1,
?0(C(?)) = 6.0J K−1mol−1, ?0(CO2(g)) = 210.0 J K−1mol−1.
Assume that the enthalpies and the entropies are temperature independent.
Solution:
Answer: 935
SnO2 (s) + C(s) → CO2 + Sn
ΔH = (Δf H)P – (Δf H)R
= – 394 + 581
= + 187 KJ/mol
ΔS = (Δ S)P – (Δ S)R
= 210 + 52 – 56 – 6
= 200 J/k mol
Δ G = 187 × 1000 – 200 × T
T = [187x1000]/200 = 935 K
Question 18: An acidified solution of 0.05 MZn2+ is saturated with 0.1 M H2S. What is the minimum molar concentration (M) of H+ required to prevent the precipitation of ZnS?
Use ?sp(ZnS) = 1.25 x 10-22 and overall dissociation constant of H2S,
KNET = ?1?2 = 1 × 10-21.
Solution:
Answer: 0.2