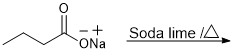Kolbe Electrolysis for Alkenes
Trending Questions
Assertion (A): SN2 reaction of an optically active aryl halide with an aqueous solution of KOH always gives an alcohol with opposite sign of rotation.
Reason (R): SN2 reactions always proceed with inversion of configuration.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true but R is false
- A is false but R is true
Explain the following with an example.
Kolbe's reaction
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Williamson ether synthesis
Unsymmetrical ether
CH3COOH + O2 =?
Identify P and Q
(I) Benzene
(II) Nitrobenzene
(III) 1, 3-Dinitrobenzene
(IV) 1, 3, 5-Trinitrobenzene
- I > II > III > IV
- I > III > II > IV
- III > I > IV > II
- IV > III > II > I

- III > I > IV > II
- III > IV > I > II
- I > III > IV > II
- III > IV > I > II
(i) Kolbes reaction.
(ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
(iii) Williamson ether synthesis.
(iv) Unsymmetrical ether.
- Sodium ethoxide + iodoethane
- Sodium ethoxide + iodomethane
- Sodium ethoxide + 2-iodopropane
- Sodium ethoxide + 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
- Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
- Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
- Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
- Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
- electrophilic substitution
- nucleophilic substitution
- nucleophilic additon
- electrophilic addition
- 4−phenylcyclopentene
- 2−phenylcyclopentene
- 1−phenylcyclopentene
- 3−phenylcyclopentene
The compound which on aqueous electrolysis liberates carbon dioxide at the anode and acetylene is:
Potassium citrate
Potassium acetate
Potassium succinate
Potassium maleate
- Product is exocyclic alkene formed according to saytzeff
- Product is exocyclic alkene formed according to Hofmann
- Product is endocyclic alkene formed according to saytzeff
- Product is endocyclic alkene formed according to Hofmann
- ethene
- ethyne
- bromoethane
- ethane
- 2, 3-hexadiene
- 2, 4-hexadiene
- 3- hexyne
- 2-hexyne
What is the reagent used and appropriate temperature required to prepare ethene from ethyl alcohol?
- Dilute H2SO4, 160∘C
- Concentrated H2SO4, 170∘C
- Dilute HCl, 170∘C
- Concentrated HCl, 160∘C
- hydrogen
- water
- oxygen
- carbon
- Acetyl chloride
- Acetaldehyde
- Acetylene
- Ethylene
- propene
- 2 - chloropropene
- allyl chloride
- ethyl chloride

- i> ii> iii> iv
- iv> iii> ii> i
- i> ii> iv> iii
- iii> iv> ii> i
- Ethanol, Ethene, Ethanoic acid
- Ethanoic acid, Ethanol, Ethylethanoate
- Ethanoic Acid, Ethanal, Ethene
- Ethanol, Ethanoic Acid, Sodium Ethanoate
- 3- Methyl-2-butene
- 2, 3-Dimethyl-1-butene
- 2-Methyl-2-butene
- 3, 4-Dimethyl-1-butene
For the following reaction, the product can be:

CH2=CH2
CH2=CH-CH2-CH=CH2
H2C=CH-CH3
A tertiary alcohol H upon acid catalyzed dehydration gives a product I. Ozonolysis of I leads to compounds J and K.Compound J upon reaction with KOH gives benzyl alcohol and a compound L, whereas K on reaction with KOH gives only M.

The structure of compound I is