From an academic perspective, understanding the difference between mitosis and meiosis is crucial. Read on to explore what is mitosis and meiosis, significant similarities and differences between the two:
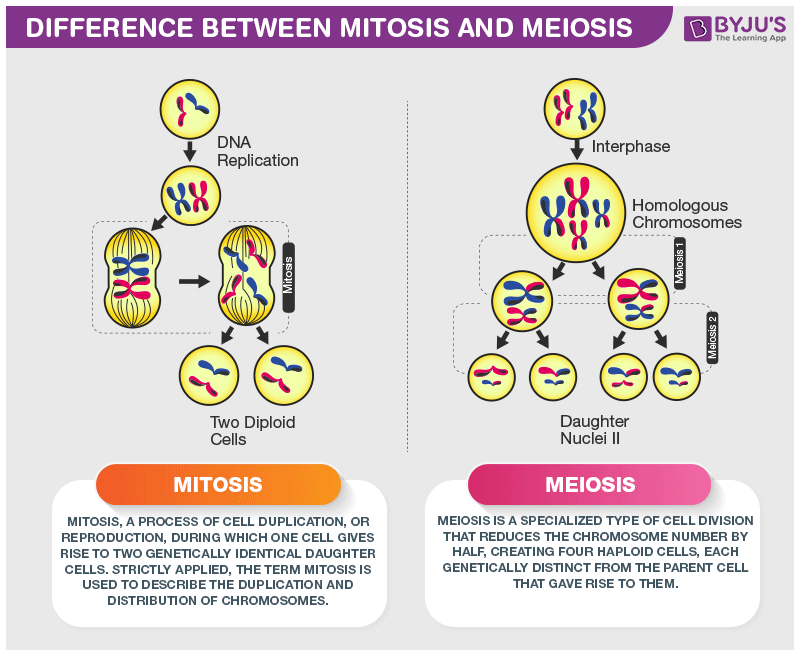
MeiosisMeiosis is a type of cell division that results in the formation of four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. |
MitosisMitosis is the type of cell division that results in the formation of two daughter cells each with the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent cell. |
Table of Contents
Difference Between Mitosis And Meiosis
Introduction
In single-celled organisms, cell reproduction gives rise to the next generation. In multicellular organisms, cell division occurs not just to produce a whole new organism but for growth and replacement of worn-out cells within the organisms.
Cell division is always highly regulated and follows a highly orchestrated series of steps. The term cytokinesis refers to the division of a cell in half, while mitosis and meiosis refer to two different forms of nuclear division.
Mitosis results in two nuclei that are identical to the original nucleus. Meiosis, on the other hand, results in four nuclei that each has ½ the chromosomes of the original cell. In animals, meiosis only occurs in the cells that give rise to the sex cells (gametes), i.e., the egg and the sperm.
Also read: Cell Cycle
Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
The important difference between mitosis and meiosis are mentioned below:
Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis |
|
|
Mitosis |
Meiosis |
Interphase |
|
| Each chromosome replicates. The result is two genetically identical sister chromatids (However, do note that interphase is technically not a part of mitosis because it takes place between one mitotic phase and the next) | Chromosomes not yet visible but DNA has been duplicated or replicated |
Prophase |
|
| Prophase –Each of the duplicated chromosomes appears as two identical or equal sister chromatids, The mitotic spindle begins to form. Chromosomes condense and thicken | Prophase I – crossing-over recombination – Homologous chromosomes (each consists of two sister chromatids) appear together as pairs. Tetrad is the structure that is formed. Segments of chromosomes are exchanged between non-sister chromatids at crossover points known as chiasmata (crossing-over) |
Metaphase |
|
| Metaphase -The chromosomes assemble at the equator at the metaphase plate | Metaphase I Chromosomes adjust on the metaphase plate. Chromosomes are still intact and arranged as pairs of homologues |
Anaphase |
|
| Anaphase – The spindle fibres begin to contract. This starts to pull the sister chromatids apart. At the end of anaphase, a complete set of daughter chromosomes is found each pole | Anaphase I Sister chromatids stay intact. However, homologous chromosomes drift to the opposite or reverse poles |
Mode of Reproduction |
|
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
Occurrence |
|
| All the cells | Reproductive cells |
Function |
|
| General growth and repair, Cell reproduction | Genetic diversity through sexual reproduction |
Cytokinesis |
|
| Occurs in Telophase | Occurs in Telophase I and in Telophase II |
Discovered by |
|
| Walther Flemming | Oscar Hertwig |
Mitosis Overview
- Mitosis is a continuous process of cell division which occurs in all types of living cells.
- Mitosis involves four basic phases – prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
- Mitosis is the process where the division of cell occurs by asexual reproduction.
- In mitosis, the nuclear membrane is broken down, spindle fibres (microtubules) attach to the chromatids at the centromere and pull apart the chromatids.
- When the chromatids reach separate ends of the cells, the spindle fibres disintegrate and a nuclear membrane rebuilds around the chromosomes making two nuclei.
- Each nucleus is identical to the original nucleus as it was in G1.
Also read: Difference between haploid and diploid
Meiosis Overview
- Meiosis is the form of nuclear cell division that results in daughter cells that have one half the chromosome numbers as the original cell.
- In organisms that are diploid, the end result is cells that are haploid. Each daughter cell gets one complete set of chromosomes, i.e., one of each homologous pair of chromosomes.
- In humans, this means the chromosome number is reduced from 46 to 23.
- The only cells that undergo meiosis will become sperm or eggs.
- The joining together of a sperm and egg during fertilization returns the number of the chromosomes to 46.
- Cells that undergo meiosis go through the cell cycle including the S phase so begin the process with chromosomes that consist of two chromatids just as in mitosis.
- Meiosis consists of meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I homologous chromosomes are separated into different nuclei.
- This is the reduction division; chromosome number is cut in half. Meiosis II is very similar to mitosis; chromatids are separated into separate nuclei.
- As in mitosis, it is spindle fibres that “pull” the chromosomes and chromatids apart.
- The end result of meiosis is four cells, each with one complete set of chromosomes instead of two sets of chromosomes.
Also read: Significance of Meiosis
Similarities Between Mitosis and Meiosis
- Both mitosis and meiosis takes place in the cell nuclei which can be observed under a microscope
- Mitosis and meiosis, both involve cell division
- Both the processes occur in the M-phase of the cell cycle. In both cycles, the typical stages are metaphase, anaphase, telophase and prophase
- In both the cycles, synthesis of DNA takes place
Also Read:
Conclusion
The difference between Mitosis and Meiosis is quite apparent. They are two very different processes that have two different functions. Meiosis is required for genetic variation and continuity of all living organisms. Mitosis, on the other hand, is focused on the growth and developments of cells. Meiosis also plays an important role in the repair of genetic defects in germline cells.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is mitosis?
2. What is Meiosis?
3. List out the difference between mitosis and meiosis,
The difference between mitosis and meiosis are as follows:
- Mitosis was discovered by Walther Flamming, while meiosis was discovered by Oscar Hertwig.
- Cytokinesis occurs only in telophase during mitosis while it occurs in Telophase 1 and telophase 2 during meiosis.
- The primary function of mitosis is general growth and repair. It is also used for cell reproduction. Meiosis, on the other hand, aims to provide genetic diversity through sexual reproduction.
- Asexual mode of reproduction is observed for mitosis. Sexual mode of reproduction is observed for meiosis.
4. State a few similarities between mitosis and meiosis.
The similarities between mitosis and meiosis are as follows:
- Mitosis and meiosis take place in the cell nuclei.
- Both involve cell division.
- Both the processes occur in the M-phase of the cell cycle.
- In both cycles, the stages are common – metaphase, anaphase, telophase and prophase.
- Synthesis of DNA occurs in both.
To know more about mitosis and meiosis, what is mitosis and meiosis, the difference between mitosis and meiosis, or any other topic in Biology, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download the BYJU’S app for further reference.



I like it. But if possible try to make it short n comfortable plzz.
This is very best I like most. This is very helpful for me.
Its Very help full
Thnxxx
????
Its very help full and best ????
Thanks so much it is very useful. Thank u so much.
Byju’s is very helpful for everyone
It is very useful for everyone. I like it very much
Useful to me, thanks BYJU’s
Use ful to me, lot of thanks BYJU’S
I like it
I like the teaching guide
Thanks, it really helps during exam times
It is very nice
This is best, helpful for everyone thanks a lot
Very understandable.
Thanks
OMG I just passed my exam with this. Thanks a lot
It is very helpful for me.
Thank u soo much
Thank u, this is so helpful
very useful for me??
Very useful it helped a lot to make assignments and studies as well. Thanks a lot
It is very informative and easily understood able also.
I am a Byju’s lover
Thank you?
Very helpful to my studies
Thanks
Very useful! Thank you BYJUS
Please make is short. As it will be easy to remember. But there is lots of info here. ???