Neuron Definition
“Neurons are the fundamental unit of the nervous system specialized to transmit information to different parts of the body.”
What is a Neuron?
Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system. They receive and transmit signals to different parts of the body. This is carried out in both physical and electrical forms. There are several different types of neurons that facilitate the transmission of information.
The sensory neurons carry information from the sensory receptor cells present throughout the body to the brain. Whereas, the motor neurons transmit information from the brain to the muscles. The interneurons transmit information between different neurons in the body.
Also Read: Nervous System
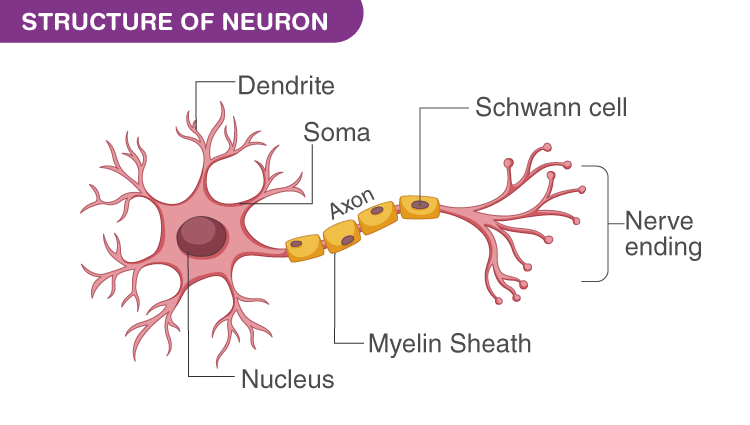
Neuron Structure
A neuron varies in shape and size depending upon their function and location. All neurons have three different parts – dendrites, cell body and axon.
Parts of Neuron
Following are the different parts of a neuron:
Dendrites
These are branch-like structures that receive messages from other neurons and allow the transmission of messages to the cell body.
Cell Body
Each neuron has a cell body with a nucleus, Golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and other components.
Axon
Axon is a tube-like structure that carries electrical impulse from the cell body to the axon terminals that passes the impulse to another neuron.
Synapse
It is the chemical junction between the terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another neuron.
Also Read: Difference between neurons and neuroglia
Neuron Types
There are three different types of neurons:
Sensory Neurons
The sensory neurons convert signals from the external environment into corresponding internal stimuli. The sensory inputs activate the sensory neurons and carry sensory information to the brain and spinal cord. They are pseudounipolar in structure.
Motor Neurons
These are multipolar and are located in the central nervous system extending their axons outside the central nervous system. This is the most common type of neuron and transmits information from the brain to the muscles of the body.
Interneurons
They are multipolar in structure. Their axons connect only to the nearby sensory and motor neurons. The help in passing signals between two neurons.
Also Read: Nerves
Neuron Functions
The important functions of a neuron are:
Chemical Synapse
In chemical synapses, the action potential affects other neurons through a gap present between two neurons known as the synapse. The action potential is carried along the axon to a postsynaptic ending that initiates the release of chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters excite the postsynaptic neurons that generate an action potential of its own.
Electrical Synapse
When two neurons are connected by a gap junction, it results in an electrical synapse. These gaps include ion channels that help in the direct transmission of a positive electrical signal. These are much faster than chemical synapses.
Also Read: Conduction of Nerve Impulse
For more information on neurons, their structure, parts and function, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.



Very good
it was so helpful thank you
very nice
Very important content and also so useful, thank you Byjus
Thank you for the great answer
Good
It helps me so much. Thanks for the answer