What is Acetone?
Acetone is a highly flammable organic compound. This organic solvent has a chemical formula C3H6O. It is also known as propanone. It is found in the exhaust from vehicles, plants, trees and forest fires. It is also found in the human body usually present in urine and blood. It is colourless and volatile. It is miscible in water, ether, ethanol and has a pungent, floral or irritating smell. It is widely used as an antiseptic and solvent. Alchemists were the first to produce acetone. It is produced with the dry distillation of metal acetates. Currently, acetone is produced by propylene either by the direct or indirect method. Almost 83% of acetone is produced during the cumene process. Also, there are other older methods to produce acetone.
Table of Content
- Structure of acetone
- General properties of acetone
- Preparation of acetone
- Chemical properties of acetone
- Uses of acetone
- Health Hazards of acetone– C3H6O
- FAQs
Structure of Acetone – C3H6O
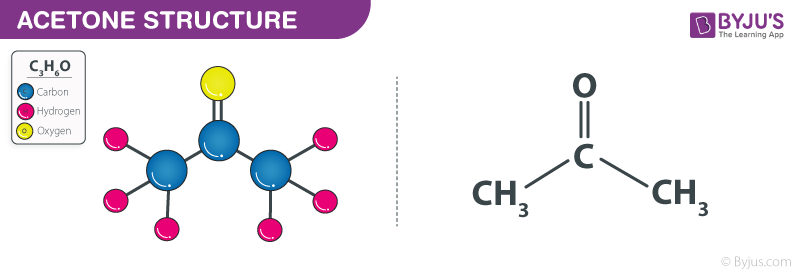
General Properties of Acetone – C3H6O
| C3H6O | Acetone |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 58.08 g/mol |
| Density | 784 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point | 56 °C |
| Melting Point | −94.7 °C |
Preparation of acetone
In the industry 83% of acetone is produced by cumene process. In the cumene process, benzene is alkylated with propylene to produce cumene, which is oxidized by air to produce phenol and acetone.
Chemical properties of acetone
Keto/enol tautomerism:
Acetone shows keto-enol tautomerism.

Haloform Reaction
Acetone undergoes haloform reaction due to presence of CH3-C=O group, it reacts with halogen in presence of alkali to form haloform and acid salt.

C3H6O Uses (Acetone)
- It is used as a solvent for synthetic fibres and plastics
- It is used as a precursor for methyl methacrylate
- It is used to prepare metal before painting
- It is used in pharmaceutical industries in some drugs
- It is volatile and hence used in the laboratory to rinse lab glassware
- It is used as a drying agent
- It is used in the defatting process
- It is used in cosmetics such as nail polish remover
- It is used in the treatment of acne
Health Hazards of acetone – C3H6O
- Acetone is highly flammable but is generally recognized to have low acute and chronic toxicity. If inhaled, acetone could cause a sore throat or cough.
- Breathing moderate to high amounts of acetone for a short amount of time can irritate your nose, throat, lungs and eyes.
- It can also cause headaches, dizziness, confusion, a faster pulse, nausea, vomiting, effects on the blood, passing out and possible coma, and a shorter menstrual cycle in women.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What are the uses of acetone?
Acetone is widely used as an industrial solvent. It also serves as a precursor to methyl methacrylate. This process begins with the conversion of acetone into acetone cyanohydrin. Many synthetic fibres and plastics can be dissolved in acetone.
How is acetone produced?
Acetone is derived from propylene, directly or indirectly. The cumene cycle produces approximately 83 per cent of the global acetone production. As a result, the production of acetone is tied to the development of phenols. Benzene is alkylated with propylene in the cumene cycle to obtain cumene, which is oxidized by the environment to create phenol and acetone.
Comment on the keto-enol tautomerism exhibited by acetone
As is the case with most ketones, acetone exhibits keto-enol tautomerism in which the “keto” structure (CH3)2C= O is in equilibrium with the enol (CH3)C(OH)=(CH2) structure. Just 0.00000024 per cent of the molecules are in the form of enol in acetone vapour at room temperature.
Is acetone used as nail polish remover?
Acetone is a powerful solvent that is used as nail polish remover. Acetone is also effective for oil removal and preparing nail polish.
Is acetone toxic?
Breathing moderate to high amounts of acetone for a short amount of time can irritate your nose, throat, lungs and eyes. It can also cause headaches, dizziness, confusion, a faster pulse, nausea, vomiting, effects on the blood, passing out and possible coma, and a shorter menstrual cycle in women.
Also, Read:
| Urea | Sucrose |
| Glucose | Phenol |
Learn more about the properties, production and the structure of C3H6O from the expert faculties at BYJU’S.





Comments