High density polyethylene, often abbreviated to HDPE, is a polymer whose monomer is ethylene. It is a thermoplastic with a very high strength to density ratio. HDPE is a very versatile plastic that has a wide range of applications – from pipes to storage bottles. When compared to other plastics, the melting point of high density polyethylene is relatively high.
Structure
HDPE is a type of polyethylene, the most common plastic which accounts for over 34% of the global plastic market. It is a polymer made up of a huge number of repeating units (known as monomers), and its chemical formula can be generalized as (C2H4)n. The branching in high density polyethylene is of a relatively low degree (when compared to other categories of polyethylene). The general structure of HDPE is illustrated below.
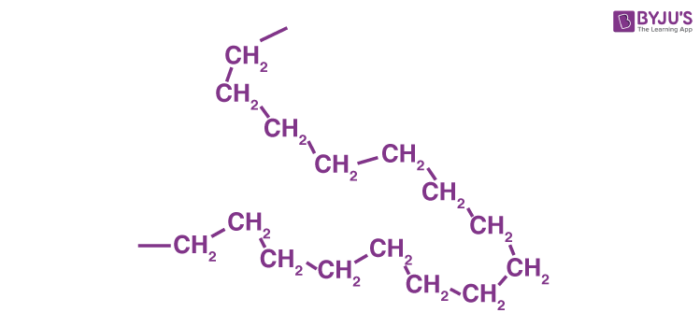
High density polyethylene is a hydrocarbon polymer that can be prepared from ethylene via a catalytic process. Some common catalysts used here include Ziegler–Natta catalysts, chromium/silica catalysts (Phillips catalyst), and metallocene catalysts.
Generally, in the polymerization process, these catalysts form free radicals at the end of the growing polyethylene molecules. They also add new ethylene monomers at the end of the molecules thereby forming a long linear chain.
HDPE mostly features a low degree of branching where the linear molecules or the polymer chains are packed together tightly. The presence of a strong intermolecular force results in a dense, highly crystalline material. However, the true mechanism of the synthesis of high-density polyethylene is still a debated topic.
Why is HDPE so Popular?
Products made of high density polyethylene are long-lasting and easy to maintain. Food stored in HDPE containers does not get contaminated by the polymer, making it quite safe for humans. Some important attributes of this polymer are highlighted in this subsection.
Moldability
- HDPE retains its rigid structure until its melting point is reached.
- Once in the melt state, this polymer can be easily molded into any desired shape.
- This property makes it an ideal choice in the production of food containers, water bottles, and plastic lumber.
Resistance to Corrosion
- This polymer is resistant to mould and rotting, making it an ideal choice for making underground water pipes.
- Since HDPE can be sterilized via boiling, it is safe to use for food containing purposes.
- Its resistance to many chemicals, such as mineral acids and cleaning fluids, make it easy to maintain. It is also resistant to many common solvents and acids.
Strength to Density Ratio
- The density of this polymer ranges from 930 kg/m3 to 970 kg/m3.
- The structure of HDPE is linear and it contains very little branching, resulting in stronger intermolecular forces.
- The tensile strength of high-density polyethylene is very high – it can withstand heavier loads than most of the other types of polyethylene.
Recyclable
- The resin identification code of HDPE is 2, it can be recycled easily.
- Despite being non-biodegradable, it is still considered an environmentally responsible plastic.
- Recycled HDPE is used in plastic furniture, automobile parts.
To summarize, high-density polyethylene owes its popularity to its low weight, high tensile strength, high impact resistance, resistance to chemicals and high temperatures, and its ability to be easily molded.
What are the Applications of HDPE?
The numerous advantages of this polymer make it an ideal choice in the production of many materials. Some uses of HDPE are listed below.
- Bottle caps and bottles are made of this polymer.
- It is also used in 3-D printing filaments
- HDPE is used in the fuel tanks of several types of automobiles.
- The piping system responsible for the distribution of natural gas is generally made of this polymer due to its resistance to corrosion and other attributes.
- It is used in plastic lumber and wood plastic composites.
- Skeletal and facial reconstruction surgeries (part of plastic surgery) involve the use of HDPE
To learn more about high density polyethylene and other important polymers, such as Teflon, register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.




Comments