We all know that electrons in an atom or a molecule absorb energy and get excited, they jump from lower energy level to higher energy level, and they emit radiations when they come back to their original states. This phenomenon accounts for the emission spectrum through hydrogen too, better known as hydrogen emission spectrum. When an electric discharge is passed through a gaseous hydrogen molecule, the hydrogen atoms in the molecule dissociate. This leads to the emission of electromagnetic radiation by the energetically excited hydrogen atoms. The hydrogen emission spectrum consists of radiations of discrete frequencies. These series of radiations are named after the scientists who discovered them.
Hydrogen emission spectrum series:
In the year 1885, on the basis of experimental observations, Balmer proposed the formula for correlating the wave number of the spectral lines emitted and the energy shells involved. This formula is given as:
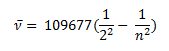
This series of the hydrogen emission spectrum is known as the Balmer series. This is the only series of line in the electromagnetic spectrum that lies in the visible region. The value, 109,677 cm-1, is called the Rydberg constant for hydrogen. The Balmer series is basically the part of hydrogen emission spectrum responsible for the excitation electron comes from higher energy shell to the second shell. Similarly, other transitions also have their own series names. Some of them are listed below,
- Comes from other higher shell to first shell-Lyman series
- Comes from other higher shell to second shell- Balmer series
- Comes from other higher shell to third shell- Paschen series
- Comes from other higher shell to 4th shell- Bracket series
- Comes from other higher shell to 5th shell- Pfund series
Johannes Rydberg, a Swedish spectroscopist, derived a general formula for the calculation of wave number of hydrogen spectral line emissions due to the transition of an electron from one orbit to another. The general formula for hydrogen emission spectrum is given by:
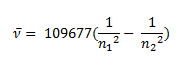
Where,
n1 = 1,2,3,4 …
n2 = n1 +1
ν= wave number of electromagnetic radiation. The value 109,677 cm-1 is known as Rydberg constant for hydrogen.
To learn more about hydrogen emission spectrum download BYJU’S – The Learning App.




excellent & understandable