What is Sodium Carbonate?
Sodium carbonate is an inorganic chemical compound. Sodium carbonate is what is commonly known as Soda ash. Soda ash is extracted from trona. Trona is a double salt containing sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate formed as a result of the series of evaporation processes taking place at lakes.
Sodium carbonate often called washing soda or soda ash is the most important of all basic heavy chemicals. Its great advantage over sodium hydroxide is that it is no-corrosive and is, therefore, safer to handle.
Recommended Videos

Sodium Carbonate Formula
Sodium carbonate is a diazonium salt of carbonic acid with chemical formula Na2CO3. It is also known as Soda crystals, soda ash, washing soda. This inorganic compound is water-soluble and when dissolved in water, it forms carbonic acid and sodium hydroxide. In its pure form, it is white powder and odourless. It is a strong base and acts as an antacid.
Sodium carbonate can be produced by four processes – “Solvay process, Labnac process, Dual-process, Electrolytic process”. Since it is a weak acid it is slightly soluble in ethanol and insoluble in alcohol. One of the important uses of Na2CO3 is as a water softener. pH is about 11.
Synthesis of Sodium Carbonate – Na2CO3
Sodium carbonate is now exclusively manufactured by the Solvey process. In this process carbon dioxide and ammonia are passed into a cold saturated solution of sodium chloride. In the reactions which occur sodium hydrogen carbonate is formed which is only very slightly soluble in the presence of sodium ions, is almost completely precipitated. It is removed by filtration and ignited to produce sodium carbonate.
The ingredients of this process are readily available and inexpensive. These are salt brine (NaCl), ammonia (NH3) and limestone (CaCO3). In this process, CaCl2 is an important by-product obtained.
The reactions can be represented by the following equation.
2NH3 + H2O + CO2 → (NH4)2CO3
(NH4)2CO3 + H2O + CO2 → 2NH4HCO3
Addition of common salt to the solution containing NH4+ and HCO3– results in the precipitation of NaHCO3 which is least soluble. It is then filtered off.
NH4HCO3 + NaCl → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
Sodium bicarbonate is then heated to give Na2CO3.
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
The CO2 gas evolved can be reused again.
Anhydrous sodium carbonate is dissolved in water and recrystallizes to get washing soda crystals containing 10 molecules of water of crystallization.
Properties of Sodium Carbonate – Na2CO3
| Na2CO3 | Sodium Carbonate |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 105.9888 g/mol |
| Density | 2.54 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point | 1,600 °C |
| Melting Point | 851 °C |
Chemical Properties of Sodium Carbonate – Na2CO3
1. Anhydrous sodium carbonate is stable towards heat. It melts without decomposition at 852oC.
2. Aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate are mildly alkaline due to hydrolysis which releases OH–(aq) ions.
Na2CO3(s) + 2H2O(l) → H2CO3(aq) + 2Na+(aq) + 2OH–(aq)
3. Aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate absorb carbon dioxide from the air forming sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Na2CO3(aq) + H2O + CO2(g) → 2NaHCO3(aq)
4. Sodium carbonate reacts with acids like weak vegetable acids, such as lime juice liberating carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3(aq) + 2H+(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Na2CO3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
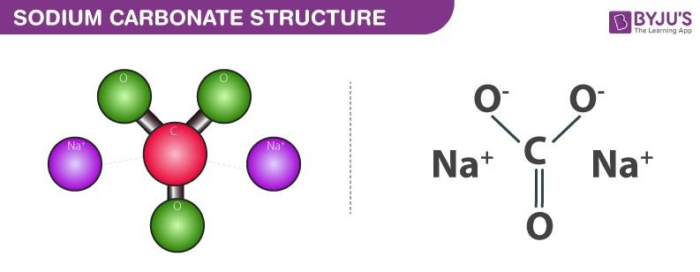
Sodium Carbonate Structure – Na2CO3
The structure of sodium carbonate molecules is illustrated below. It can be noted that each molecule of sodium carbonate contains 2 sodium atoms, 3 oxygen atoms and one carbon atom. Each sodium cation holds a charge of +1 whereas the polyatomic carbonate anion holds a net charge of magnitude -2. Sodium carbonate is, therefore, a neutrally charged molecule.
Uses of Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
The uses of sodium carbonate are listed below.
- It is used in the manufacture of detergents, soaps, paper.
- Also used in the manufacture of water glass (sodium silicate), borax, sodium phosphate, and many other sodium compounds.
- It is used in as a wetting agent in brick industry
- It is used as an abrasive and foaming agent in toothpaste
- It is used as a pH modifier
- It is used as water softener – Hard water which consists of magnesium and calcium ions are precipitated by carbonate.
- As a laboratory reagent to standardize acids and as an analytical reagent.
Also, Read: Preparation of Standard Solution of Sodium Carbonate
FAQs
1. What is the common name of sodium carbonate?
Ans: The inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 is sodium carbonate, Na2CO3, also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals.
2. Mention the hazards of sodium carbonate?
Ans: Sodium carbonate may pose a number of health and safety hazards. This chemical’s inhalation can result in adverse effects such as irritation of the respiratory tract, coughing, shortness of breath, and pulmonary edema.
3. What is anhydrous sodium carbonate?
Ans: Hydrated sodium carbonate has the formula Na2C03.nH20. 0n strong heating, hydrated sodium carbonate decomposes completely into water and anhydrous sodium carbonate, Na2C03.
4. What is sodium carbonate used for?
Ans: As water softener, food processing aid, pH modifier, chemical swimming pool and electrolyte are the primary uses of sodium carbonate.
5. Where is sodium carbonate found?
Ans: It is discovered in big natural deposits and mined in Wyoming; it is also retrieved from lake brines in California (with other chemicals). The main uses of sodium carbonate are glass manufacturing and chemical manufacturing.
Learn more about the chemical behaviour and importance of Na2CO3 with the expert faculties at BYJU’S.




nice
thanks for ur articles#