JEE Main 2020 Paper with Solutions Chemistry - Shift 1 will highlight the difficulty level of the paper, section-wise analysis as per different slots, most asked topics and types of questions asked. Practising these questions will help the candidates to determine the possible difficulty level of the JEE Main examination. These papers will assist them in understanding the amount of preparation required to face the examination.
September 4 Shift 1 - Chemistry
Question 1: The IUPAC name of the following compound is:
- 1) 3-Bromo-5-methyl cyclopentane carboxylic acid
- 2) 4-Bromo-2-methyl cyclopentane carboxylic acid
- 3) 5-Bromo-3-methyl cyclopentanoic acid
- 4) 3-Bromo-5-methyl cyclopentanoic acid
Solution:
-
Answer: (2)

4–Bromo-2-methyl cyclopentane carboxylic acid
Question 2: On heating, lead(II) nitrate gives a brown gas (A). The gas (A) on cooling changes to a colourless solid/liquid (B). (B) on heating with NO changes to a blue solid (C). The oxidation number of nitrogen in solid (C) is:
- 1) +3
- 2) +4
- 3) +2
- 4) +5
Solution:
-
Answer: (1)
Pb(NO3)2 → PbO + NO2 + O2
(A)
Brown gas
2NO2 → N2O4 [on cooling]
(C)
colourless solid

(C)
blue solid
Question 3: The ionic radii of O2–, F–, Na+ and Mg2+ are in the order:
- 1) F– > O2– > Na+ > Mg2+
- 2) Mg2+ > Na+ > F– > O2–
- 3) O2– > F– > Na+ > Mg2+
- 4) O2– > F– > Mg2+ > Na+
Solution:
-
Answer: (3)
O2– > F– > Na+ > Mg2+
Question 4: When neopentyl alcohol is heated with an acid, it is slowly converted into an 85:15 mixture of alkenes A and B, respectively. What are these alkenes?
Solution:
-
Answer: (3)

Question 5: The region in the electromagnetic spectrum where the Balmer series lines appear is:
- 1) Microwave
- 2) Infrared
- 3) Ultraviolet
- 4) Visible
Solution:
-
Answer: (4)
The question should be a bonus as lines of the Balmer series belong to both UV as well as visible regions of the EM spectrum. However most appropriate should be the visible region.

Question 6: Identify the incorrect statement from the options below for the above cell:
- 1) If Eext = 1.1 V, no flow of e– or current occurs
- 2) If Eext > 1.1 V, Zn dissolves at Zn electrode and Cu deposits at Cu electrode
- 3) If Eext > 1.1 V, e– flow from Cu to Zn
- 4) If Eext < 1.1 V, Zn dissolves at the anode and Cu deposits at the cathode
Solution:
-
Answer: (2)
Question 7: What are the functional groups present in the structure of maltose?
- 1) One acetal and one hemiacetal
- 2) One acetal and one ketal
- 3) One ketal and one hemiketal
- 4) Two acetals
Solution:
-
Answer: (1)

Question 8: Match the following:
| (i) Foam | (a) smoke |
| (ii) Gel | (b) cell fluid |
| (iii) Aerosol | (c) jellies |
| (iv) Emulsion | (d) rubber |
| (e) froth | |
| (f) milk |
- 1) (i)-(e), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(f)
- 2) (i)-(b), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(e), (iv)-(d)
- 3) (i)-(d), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(e)
- 4) (i)-(d), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(e), (iv)-(f)
Solution:
-
Answer: (1)
Foam → Froth, whipped cream, soap lather
Gel → Cheese, butter, jellies
Aerosol → smoke dust
Emulsion → milk
Sol → Cell fluid
rubber → Solid form
froth → form
(i) - e, (ii) - c, (iii) - a, (iv) - f
Question 9: An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C6H12O2) was hydrolysed with dilute H2SO4 to give a carboxylic acid (B) and alcohol (C). ‘C’ gives white turbidity immediately when treated with anhydrous ZnCl2 and conc. HCl. The organic compound (A) is:
Solution:
Question 10: Among the statements (a)-(d), the correct ones are:
(a) Limestone is decomposed to CaO during the extraction of iron from its oxides.
(b) In the extraction of silver, silver is extracted as an anionic complex.
(c) Nickel is purified by Mond’s process.
(d) Zr and Ti are purified by Van Arkel method.
- 1) (c) and (d) only
- 2) (b), (c) and (d) only
- 3) (a), (b), (c) and (d)
- 4) (a), (c) and (d) only
Solution:
-
Answer: (3)
Limestone finally goes to slag formation
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
Slag
Question 11: For one mole of an ideal gas, which of these statements must be true?
(a) U and H each depends only on temperature
(b) Compressibility factor z is not equal to 1
(c) CP,m – CV,m = R
(d) dU = CV dT for any process
- 1) (a), (c) and (d)
- 2) (a) and (c)
- 3) (c) and (d)
- 4) (b), (c) and (d)
Solution:
-
Answer: (1)
For ideal gas
?v / ?v|T = 0 & ?H / ?v|T = 0
(a) Hence function of temperature only.
(b) Compressibility factor (z) = 1 Always
(c) Cp,m – CV,m = R
(d) dv = nCv,m dT for all process
The answers are a, c, d.
Question 12: [P] on treatment with Br2 / FeBr3 in CCl4 produced a single isomer C8H7O2Br while heating [P] with soda lime gave toluene. The compound [P] is:
Solution:
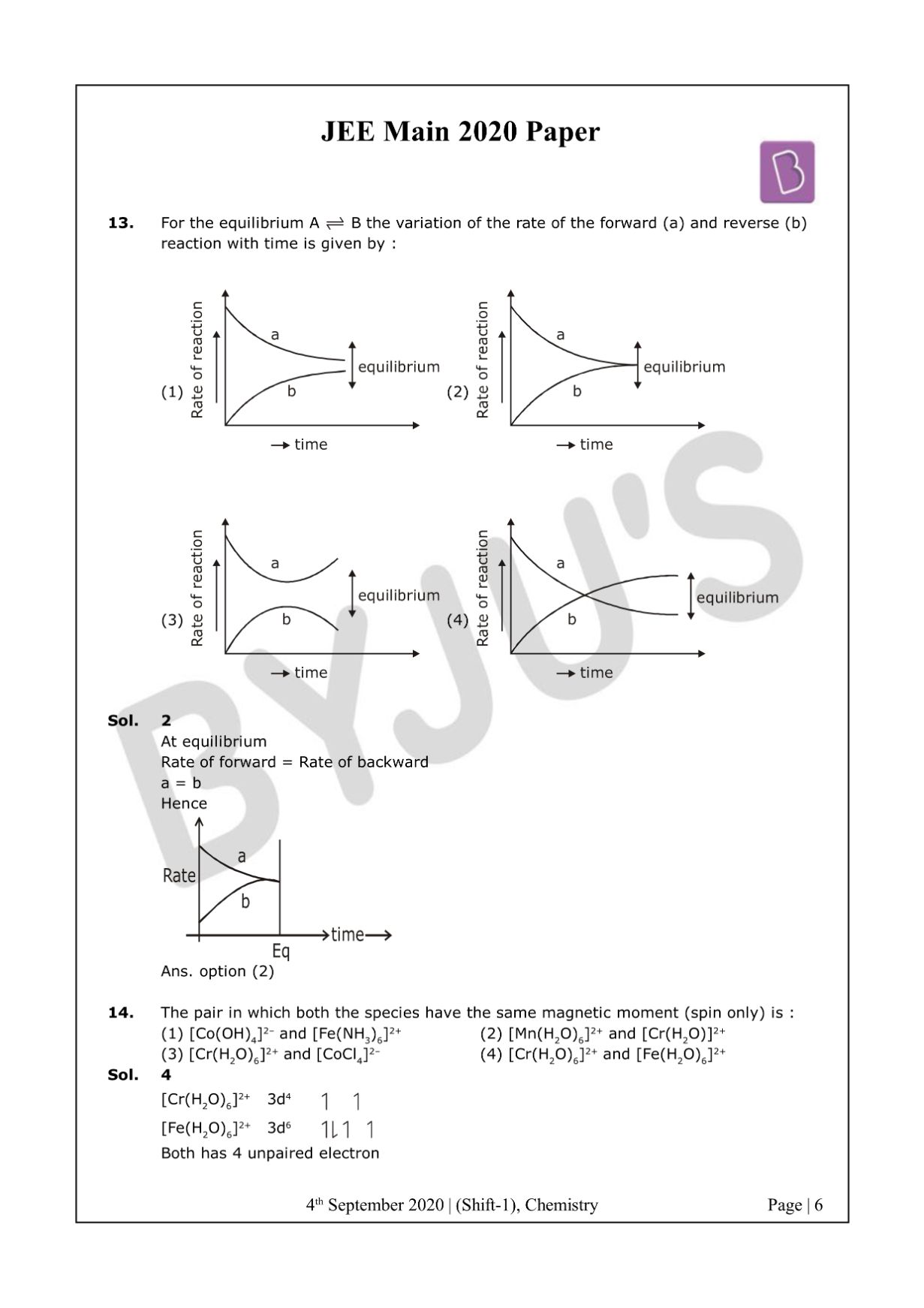
Question 13: For the equilibrium A ⇌ B the variation of the rate of the forward (a) and reverse (b) reaction with time is given by :
Solution:
-
Answer: (2)
At equilibrium
Rate of forward = Rate of backward
a = b
Hence

The answer is option 2.
Question 14: The pair in which both the species have the same magnetic moment (spin only) is:
- 1) [Co(OH)4]2– and [Fe(NH3)6]2+
- 2) [Mn(H2O)6]2+ and [Cr(H2O)]2+
- 3) [Cr(H2O)6]2+ and [CoCl4]2–
- 4) [Cr(H2O)6]2+ and [Fe(H2O)6]2+
Solution:
-
Answer: (4)

Both have 4 unpaired electrons.
Question 15: The number of isomers possible for [Pt(en)(NO2)2] is:
- 1) 2
- 2) 3
- 3) 4
- 4) 1
Solution:
-
Answer: (2)
Three linkage isomers:
[Pt(en)(NO2)2]
[Pt(en)(ONO)2]
[Pt(en)(NO2)(ONO)]
Question 16: The decreasing order of reactivity of the following organic molecules towards the AgNO3 solution is:

- 1) (B) > (A) > (C) > (D)
- 2) (A) > (B) > (C) > (D)
- 3) (A) > (B) > (D) > (C)
- 4) (C) > (D) > (A) > (B)
Solution:
-
Answer: (1)

Order or stability
(B) > (A) > (C) > (D)
Question 17: The intermolecular potential energy for the molecules A, B, C and D given below suggests that:

- 1) A–A has the largest bond enthalpy.
- 2) D is more electronegative than other atoms.
- 3) A–D has the shortest bond length.
- 4) A–B has the stiffest bond.
Solution:
-
Answer: (4)
As EA–B is the highest, the answer is option 4.
Question 18: Which of the following will react with CHCl3 + alc. KOH?
- 1) Thymine and proline
- 2) Adenine and thymine
- 3) Adenine and lysine
- 4) Adenine and proline
Solution:
-
Answer: (3)
CHCl3 + Alc. KOH reacts with those compounds which have a –NH2 group.

Question 19: The elements with atomic numbers 101 and 104 belong to, respectively:
- 1) Actinoids and Group 6
- 2) Group 11 and Group 4
- 3) Group 6 and Actinoids
- 4) Actinoids and Group 4
Solution:
-
Answer: (4)

The answer is Actinoids & 4th group.
Question 20: On combustion of Li, Na and K in excess of air, the major oxides formed, respectively, are :
- 1) Li2O2, Na2O2 and K2O2
- 2) Li2O, Na2O2 and KO2
- 3) Li2O, Na2O and K2O2
- 4) Li2O, Na2O2 and K2O
Solution:
-
Answer: (2)
Li2O, Na2O2 and KO2
Question 21: The number of chiral centres present in [B] is ________.

Solution:
-
Answer: (4)

4 chiral centres are present in the final product.
Question 22: At 300 K, the vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of n-hexane and 3 moles of n-heptane is 550 mm of Hg. At the same temperature, if one more mole of n-heptane is added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm of Hg. What is the vapour pressure in mm of Hg of n-heptane in its pure state _______?
Solution:
-
Answer: 600

Question 23: The mass of ammonia in grams produced when 2.8 kg of dinitrogen quantitatively reacts with 1 kg of dihydrogen is _________.
Solution:
-
Answer: 3400
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
2800g 1000g
100 mol 500 mol
L.R. mole of NH3 produced = 200 mol
mass = 3400 g
Question 24: If 75% of a first order reaction was completed in 90 minutes, 60% of the same reaction would be completed in approximately (in minutes) ________. (take : log 2 = 0.30; log 2.5 = 0.40)
Solution:
-
Answer: 60
t75% = 90 min = 2 × t1/2
t1/2 = 45 min
[ln (2) / 45] × 60% = ln [100 / 40]
t60% = 45 × [0.4 / 0.3]
t60% = 60 min
Question 25: A 20.0 mL solution containing 0.2 g impure H2O2 reacts completely with 0.316 g of KMnO4 in acid solution. The purity of H2O2 (in %) is _______ (mol. wt. of H2O2 = 34’ mole wt. of KMnO4 = 158)
Solution:
-
Answer: 85
H2O2 + KMnO4 → Mn+2 + O2
[moles of H2O2] × 2 = [0.316 / 158] * 5
moles of H2O2 = 5 × 10–3
mass of H2O2 = 170 × 10–3 g
% purity = {[170 * 10-3] / 0.2} * 100 = 85%