We know that electromagnetism is an important branch of Physics that deals with electromagnetic force. It typically deals with magnetic force and electric current. Let us know about the law that relates magnetic fields to the electric current – Biot-Savart Law.
| Table of Contents |
What is Biot-Savart Law?
Biot-Savart’s law is an equation that gives the magnetic field produced due to a current carrying segment. This segment is taken as a vector quantity known as the current element.
What is the Formula of Biot-Savart’s Law?
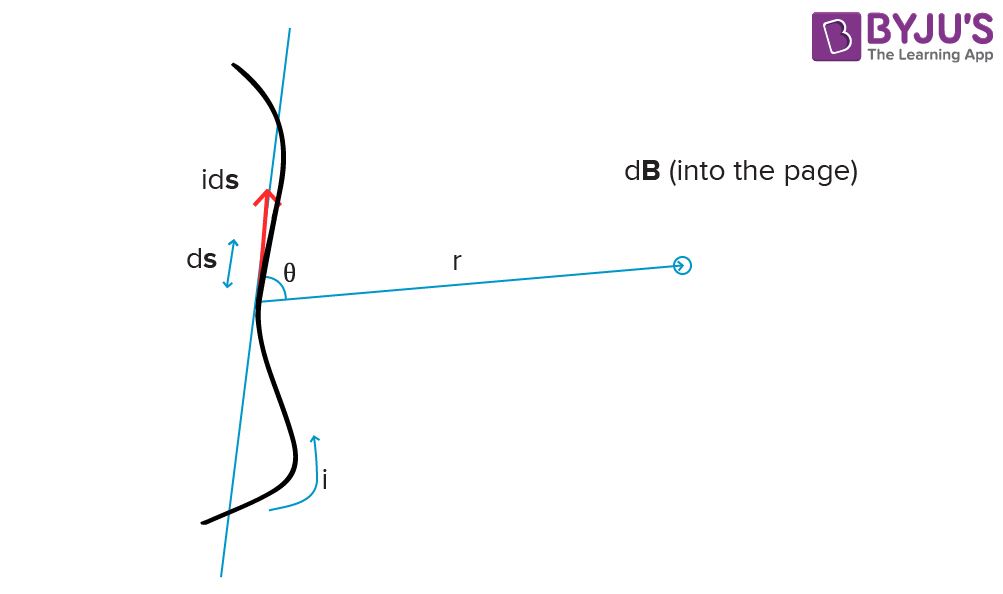
Consider a current carrying wire ‘i’ in a specific direction as shown in the above figure. Take a small element of the wire of length ds. The direction of this element is along that of the current so that it forms a vector i ds.
To know the magnetic field produced at a point due to this small element, one can apply Biot-Savart’s Law. Let the position vector of the point in question drawn from the current element be r and the angle between the two be θ. Then,
\(\begin{array}{l}\left | dB \right |=(\frac{\mu _{0}}{4\pi })(\frac{Idlsin\Theta }{r^{2}})\end{array} \) |
Where, μ0 is the permeability of free space and is equal to 4π × 10-7 TmA-1.
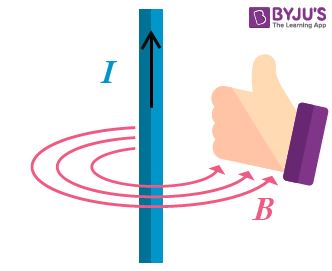
The direction of the magnetic field is always in a plane perpendicular to the line of element and position vector. It is given by the right-hand thumb rule where the thumb points to the direction of conventional current and the other fingers show the magnetic field’s direction.
This can be expressed in terms of vectors as:
d→B = μ04π i →ds ×^rr2
Let us use this law in an example to calculate the Magnetic field due to a wire carrying current in a loop.
Example of Biot-Savart’s Law
The magnetic field of Current Loop:
Consider a current loop of radius R with a current ‘i’ flowing in it. If we wish to find the electric field at a distance l from the center of the loop due to a small element ds, we can use the Biot-Savart Law as:
d→B = μ04π i d→s ×^rr2
Consider the current element ids at M which is coming out of a plane in the figure. Since r is in the plane of the page, the two of them are perpendicular to each other. Furthermore, the magnetic field produced db is also in the plane of the page.
dB = μ04π i ds . 1. sin 90⁰r2 = μ04π i dsr2
But from the figure,
R2 + l2 = r2
dB = μ04π i dsR2 + l2
Now, if we consider the diametrically opposite element at N, it produces a field such that it’s component perpendicular to the axis of the loop is opposite to that of the field produced at M. Thus, only the axial components remain. We can divide the loop into diametrically opposite pairs and apply the same logic.
Also, note that from the figure that
α = θ
∴ cos θ = R√R2 + l2
Thus,
dB cos θ = μ04π i dsR2 + l2 × R√R2 + l2
The total field will be thus,
B = ∫ μ04π i ds R(R2 + l2)32 = μ04π i R(R2 + l2)32 ∫ ds
B = μ04π i R(R2 + l2)32 × 2πR
B = μ0 i R22(R2 + l2)32
The right-hand thumb rule can be used to find the direction of magnetic field.
Related Articles:
Applications of Biot-Savart’s Law
Some of Biot-Savart’s Law applications are given below.
- We can use Biot–Savart law to calculate magnetic responses even at the atomic or molecular level.
- It is also used in aerodynamic theory to calculate the velocity induced by vortex lines.
Importance of Biot-Savart Law
Following are the importance of the Biot-Savart law:
- Biot-Savart law is similar to Coulomb’s law in electrostatics.
- The law is applicable for very small conductors too which carry current.
- The law is applicable for symmetrical current distribution.
Solved Problems on Biot-Savart Law
Q1. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic field of a wire loop at the center of the circle with radius R and current I.
Ans: The magnitude of the magnetic field of the wire loop is given as:
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{\mu _{0}I}{2R}\end{array} \) |
Q2. A circular coil of radius 5 × 10-2 m and with 40 turns is carrying a current of 0.25 A. Determine the magnetic field of the circular coil at the center.
Ans: The radius of the circular coil = 5 × 10-2 m
Number of turns of the circular coil = 40
Current carried by the circular coil = 0.25 A
Magnetic field is given as:
=
= 1.2 × 10-4 T
Q3. Determine the magnetic field at the center of the semicircular piece of wire with a radius 0.20 m. The current carried by the semicircular piece of wire is 150 A.
Ans: The radius of the semicircular piece of wire = 0.20 m
Current carried by the semicircular piece of wire = 150 A
Magnetic field is given as:
The differential form of Biot-Savart law is given as:
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Which law of electricity is Biot Savart law of magnetism analogous to?
Biot-Savart law in magnetism is analogous to Coulomb’s law in electricity. According to Biot Savart law, magnetic flux density
Name one property that cannot be calculated using the Biot Savart law.
Electric field intensity cannot be calculated using the Biot Savart law. It is used for calculating the magnetic field intensity. Which is further used for calculating the flux density and permeability using the formula
Consider a circular conductor with 2m radius and 8A current flowing through it. Determine the magnetic field intensity at the centre of the circular conductor.
By using the formula
Substituting the values for current I = 8A and radius R = 2m, we get B =
What is the magnetic field at the centre of the conductor when the conductor is subjected to a current of 9A and with infinite radius?
The formula used for calculating the magnetic field is
Can electric field intensity be computed using Biot Savart’s Law?
Here is a video lecture of Biot Savart for you!