Electricity and magnetism are one of the most interesting topics in physics. In this article, we will learn about the concepts of magnetism and electricity and the relationship between them. We shall also learn the magnetism and electricity definition, interesting concepts like electron movement, conductors, semiconductor and insulators, and magnetic field.
| Table of Contents: |
What is Electricity?
Electricity is the presence and motion of charged particles. How does energy travel through copper wire and through space? What is electric current, electromotive force, and what makes a landing light turn on or a hydraulic pump motor run? Each of these questions requires an understanding of many basic principles. By adding one basic idea on top of other basic ideas, it becomes possible to answer most of the interesting and practical questions about electricity or electronics. Our understanding of electric current must begin with the nature of matter. All matter is composed of molecules. All molecules are made up of atoms, which are themselves made up of electrons, protons, and neutrons.

See the video below to know about electricity.
Electron Movement
Conductors
Insulators
These are materials that do not conduct electrical current very well or not at all. Good examples of these are glass, ceramic, and plastic. Under normal conditions, atoms in these materials do not produce free electrons. The absence of the free electrons means that electrical current cannot be conducted through the material. Only when the material is in an extremely strong electrical field will the outer electrons be dislodged. This action is called breakdown and usually causes physical damage to the insulator.
Semiconductors
What is Magnetism?
Magnetism is a concept introduced in physics to help you understand one of the fundamental interactions in nature, the interaction between moving charges. Like the gravitational force and the electrostatic force, the magnetic force is an interaction at a distance.
See the video below to know about magnetism.

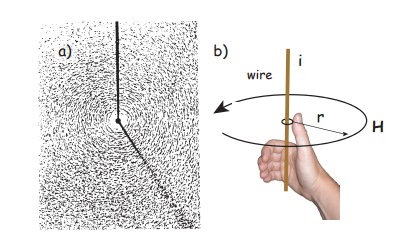
What is a Magnetic Field?
| Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current | Magnetic Field Of Earth – Earth’s Magnetism |
| Electromagnetism | Current Electricity |
Difference Between Electricity and Magnetism
There are numerous ways by which we can differentiate between magnetism and electricity. Some main electricity and magnetism differences are given in the points mentioned below.
- The major difference between electricity and magnetism is the presence of magnetism.
- Electricity can be present in a static charge, while magnetism’s presence is only felt when there are moving charges as a result of electricity.
- In simple words, electricity can exist without magnetism, but magnetism cannot exist without electricity.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are the types of electricity?
There are basically two types of electricity, Static electricity and Current electricity
What are the sources of electricity?
The various sources of electricity are solar energy, fossil fuels, nuclear power, wind energy and hydroelectric power.
What is the unit of the magnetic field?
Magnetic field is denoted by B and H. The SI unit of H is amperes per meter and the SI unit of B is Newtons per meter per ampere or Teslas.
What is the basic law of magnetism?
The basic law of magnetism is that the unlike poles attract and like poles repel.
What is electromagnetism?
Electromagnetism is associated with electric charges and the magnetic fields.
What is Faraday’s law of electromagnetism?
Faraday’s law of electromagnetism explains how magnetic field and electric charge interact to produce EMF (electromotive force).
Hope you understood magnetism and electricity definition, properties, electron movement, conductors, semiconductors, insulators, and magnetic field. To learn more interesting physics topics with the help of engaging and interactive video lessons keep visiting BYJU’S.


I think this lesson is very important for physics
i like the note but please make it by video
Nice app for learning
This is very useful for me.