Over the years, people have been using different techniques to navigate across the world. Traditionally, people used to depend on landmarks and stars to travel between different locations, while compasses and maps helped them from getting lost. The discovery of the Global Positioning System (GPS) made people no longer have to rely on these traditional positioning techniques to find their way around.
History of Global Positioning System (GPS)
GPS is also known as the Navstar project started in 1973 and became fully operational in 1994. This system is funded and run by the United States Department of Defence. Originally, this system was intended for military purposes only but was made available to public use on completion of the project. In this article, let us learn how GPS works in detail.
Space Segment:
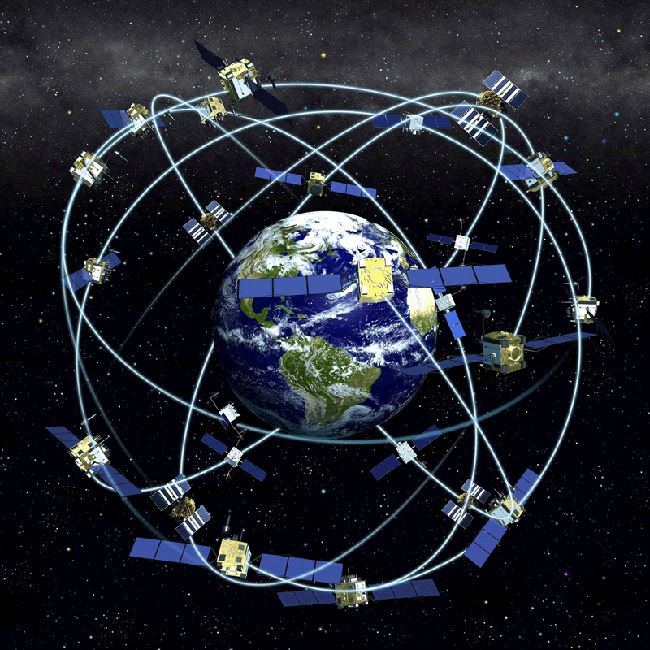
GPS consists of a network of 24 active satellites located nearly 20000 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. Each satellite broadcasts different signals which can be tracked by a GPS receiver on earth, which are then analyzed by the GPS receiver to determine its precise location. The signals operate in all weather conditions but can’t penetrate through solid objects, so GPS receivers perform best when they have a clear view of the sky.
Control Segment:
GPS contains a control segment that has a system of tracking stations located around the world. The master control facility is located at Schriever Air Force Base in Colorado. Its receivers come in all different shapes and sizes, are widespread, and are affordable. Today, GPS receivers can be found in watches, phones, tablets, computers, cars, and a wide variety of other devices. This segment consists of:
- A master control station
- An alternate master control station
- Six dedicated monitor stations
- Four dedicated ground stations
User Segment:
The GPS user segment has a user segment and GPS receivers. These receivers transform SV signals into velocity, position, and time estimates. It needs four satellites to measure the Four dimensions of X, Y, Z, and time. GPS receivers are helpful in navigation, time dissemination, positioning, and some other research. Navigation is the key function of GPS. It is useful for ships, aircraft, and even ground vehicles.
Fast Facts on Global Positioning System (GPS)
- GPS became fully operational in 1994.
- It may be free for the public to use but it costs nearly 2 million dollars for the US government.
- GPS receivers can determine your position anywhere on the Earth. Including the oceans.
- A normal GPS satellite travels nearly 14000 km per hour.
- These signals can travel through most of the plastics, but cannot pass through wood and concrete.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
GPS consists of a network of how many satellites?
GPS consists of a network of 24 satellites.
In which year GPS became operational?
GPS became operational in 1994.
Can GPS calculate the time of sunrise and sunset?
Yes
Where is GPS used?
GPS was purposely developed for which sector?
GPS was purposely developed for military purpose.
If you wish to learn more physics concepts with the help of interactive video lessons, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.


Comments