In Physics, waves are explained as an oscillation about the fixed point, which is accompanied by the transfer of energy travelling from one medium to another medium. When the transfer of energy takes place through a medium due to oscillation, the resultant wave can be termed as a mechanical wave.
The medium of transmission limits the distance of the wave’s propagation. In this case, the oscillating material moves about a fixed point, and there is very little translational motion. One interesting property of mechanical waves is the way they are measured, given by displacement divided by wavelength. This dimensionless factor when it reaches 1, results in the generation of harmonic effects. Example: waves break on the beach when this factor exceeds one, resulting in turbulence.
Table of Contents
- Types of Mechanical Waves
- Transverse Waves
- Transverse Waves Examples
- Longitudinal Waves
- Longitudinal Waves Examples

Types of Mechanical Waves
There are primarily two types of mechanical waves, namely:
- Transverse Waves
- Longitudinal Waves
What are Transverse Waves
In transverse waves, the displacement of the particle is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. Below is the picture, which explains how waves move sideways when the particles move up and down.
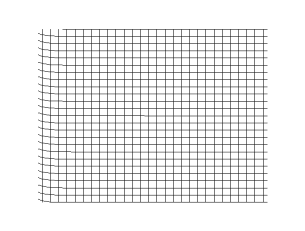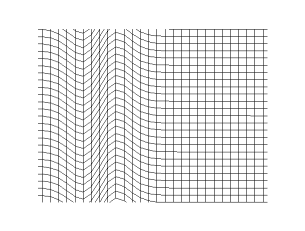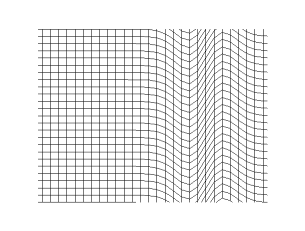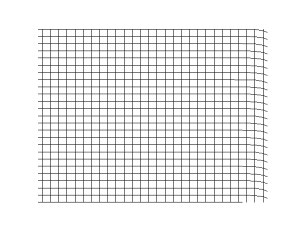
Examples Of Transverse Waves
In transverse waves too, the particles do not move along with the wave. They move up and down about their equilibrium positions. Some examples of transverse waves are:
- The ripples on the surface of the water
- The secondary waves of an earthquake
- Electromagnetic waves
- The waves on a string
- Stadium or human wave
- The ocean waves
Interested to learn more about other concepts related to waves, below is the link:
| Gravity Waves
Gravity waves are also known as gravitational waves and are defined as the ripples caused in the space. It is caused due to various reasons like two huge stars orbiting each other or the explosion of stars asymmetrically. |
| Sound Waves – Medium For Their Propagation
Sound waves are mechanical waves are defined as the motion of waves with compressions (high-pressure region) and rarefaction (low-pressure region). |
What are Longitudinal Waves
In a longitudinal wave, the displacement of the particle is parallel to the direction of the wave propagation. What you see in the picture is the wave front progressing forward and the particles compressing and expanding in the same direction. This kind of wave is marked by periodic compression zones and rarefaction zones, where the medium expands.
Examples of Longitudinal Waves
The particles in the wave do not move along with the wave though; they simply oscillate back and forth about their own equilibrium.
- Sound waves in air
- The primary waves of an earthquake
- Ultrasound
- The vibration in a spring
- The fluctuations in a gas
- The tsunami waves
Examples of Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
We have learnt the P waves (which is also known as Primary waves) are examples of longitudinal waves while the S waves (which is also known as Secondary waves) are examples of transverse waves.
Further, we shall learn about the examples that are a combination of both longitudinal waves and transverse waves.
- Water waves
Water waves are an example of a combination of both longitudinal and transverse waves. The movement of particles in water waves is in a clockwise direction. While the movement of the waves in a transverse manner. We also need to understand that the radius of the particles decreases with an increase in the depth of the water. - Rayleigh surface waves
Rayleigh surface waves is another example of a combination of both longitudinal and transverse waves. These waves involve both up and down motion as well as side to side motion. Rayleigh wave is also known as the seismic wave which causes the shaking of the earth in an elliptical motion. Of all the known seismic waves, the Rayleigh waves can produce a long wave duration on the seismographs.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about waves, oscillation and much more with interactive videos.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
State whether the given statement is true or false:
Waves can be defined as the transfer of momentum and energy via a medium.
The propagation of waves takes place only through a medium. So, it is right to say that during the propagation of the waves, there is a transfer of energy and moment from one particle to another.
State whether the given statement is true or false:
For the propagation of mechanical waves, there is no requirement of a medium.
Mechanical waves require or are dependent on the medium for their propagation. This is because the particles of these waves need a medium to propagate. Their transfer of energy takes place only through a medium. This is the reason why sound waves do not travel in a vacuum as there are no particles to transport the energy.
State whether the given statement is true or false:
The polarization phenomenon is possible in sound waves.
For the phenomenon of polarization to take place, the particles of the wave need to be perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Since sound waves are longitudinal waves, this phenomenon cannot be executed by sound waves. This is possible in light waves.
What is node in wave?
Also, a standing wave is defined as the wave in a medium that has every point associated with a constant amplitude. The amplitude in this wave is zero at the nodes while maximum at the antinodes.
What are the characteristics of transverse waves?
- The propagation of transverse waves is possible only through solids and not through liquids or gases.
- Only transverse waves can exhibit the phenomenon of polarization. The vibration of the particles in a medium takes place in the same place and this is known as the plane of vibration or polarization.
- Properties such as pressure and density are constant in a medium when there is a propagation of transverse waves.
- The formation of typical crests and troughs in transverse waves is periodic in nature.
- The propagation of transverse waves is dependent on the rigidity of the medium.


Comments