What is Nuclear Fusion?
Nuclear fusion is a reaction through which two or more light nuclei collide to form a heavier nucleus. The nuclear fusion process occurs in elements that have a low atomic number, such as hydrogen. Nuclear Fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission reaction in which heavy elements diffuse and form lighter elements. Both nuclear fusion and fission produce a massive amount of energy.
|
Nuclear Fusion Definition: Nuclear fusion is when two or more atomic nuclei fuse to form a single heavier nucleus. In the reaction, the matter is not conserved because some of the mass of the fusing nuclei is converted to energy. |
How does Nuclear Fusion take place?
Let us look at the nuclear fusion example below to understand how the fusion reaction occurs.
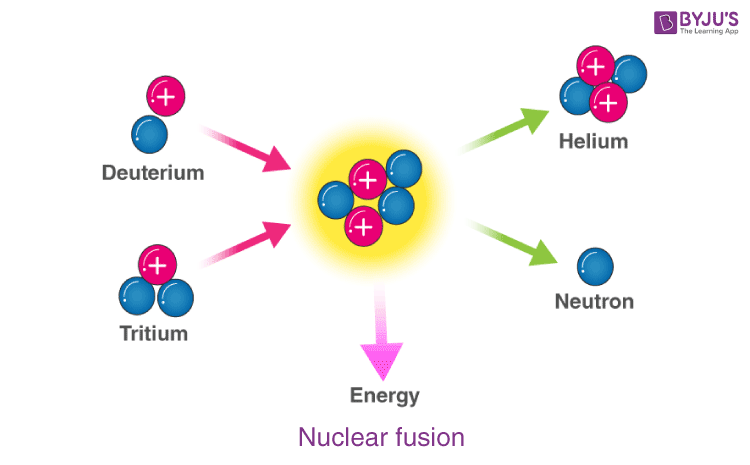
When deuterium and tritium fuse together, their components are recombined to form a helium atom and a fast neutron. As the two heavy isotopes are recombined into a helium atom and a neutron, the leftover’s extra mass is transformed into kinetic energy.
The participating nuclei should be brought together for the nuclear fusion reaction to occur. They should be brought so close to each other that the nuclear forces become active and glue to the nuclei together.
Nuclear Fusion in the Universe
Every star in the universe, including the sun, is alive due to nuclear fusion. It is through this process that they produce an enormous amount of heat and energy. The pressure at the core of any star is tremendously high, and that is where the nuclear fusion reaction occurs.

For example, the temperature at the sun’s core is around 15 million degrees Celsius. At this temperature, coupled with very high pressure, two isotopes of Hydrogen, Deuterium, and Tritium, fuse to form Helium and releases a massive amount of energy in the form of heat. Around 600 million tons of hydrogen are converted into Helium every second in the sun. The reactions which take place in the sun provide an example of nuclear fusion.
Difference Between Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion
The table below lists the major differences between fusion and fission reactions.
| Nuclear Fission | Nuclear Fusion |
| Nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction that splits a heavy atom into two or more smaller ones. | Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction that combines two or more small atoms to form a large atom. |
| It does not occur naturally. | The universe is full of instances of nuclear fusion reactions. Every star uses it to produce energy. |
| It produces a large quantity of energy. | It produces greater energy than the fission reaction. |
| Does not require a lot of energy to split an atom into two. | Requires a lot of heat and pressure for the process to happen. |
To learn the differences in detail, visit the article below:
Applications of Nuclear Fusion
We are still at an experimental stage as far as nuclear fusion reactions are concerned.
- Clean: No combustion occurs in nuclear power (fission or fusion), so there is no air pollution.
- Less nuclear waste: The fusion reactors will not produce high-level nuclear wastes like their fission counterparts, so that disposal will be less of a problem. In addition, the wastes will not be of weapons-grade nuclear materials as is the case in fission reactors.
If appropriately utilised, nuclear fusion is the answer to the world’s power crisis problem. It is clean and produces a minimal amount of nuclear waste as compared to fission reactions. In addition, the fuel for fusion, Deuterium, and Tritium, are also readily available in nature. Thus, scientists are hopeful that fusion will be a viable alternative power source in the coming centuries.
In the video, you will learn how to harness the energy produced by nuclear fusion reaction in a controlled manner.

|
Related Links: |
Important Questions on Nuclear Fusion
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is Nuclear Fusion?
What is the life span of a nuclear power station?
The usual life span of a nuclear power station is 40 years. But the modern pressurized water reactors come with a life span of 60 years.
How are nuclear accidents classified?
According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), two sub-levels categorize the accidents. The main two levels are the upper level with 4-7 sub-levels and the lower level with 1-3 sub-levels.
Name the international organization that oversees the operation of nuclear power stations.
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an international organization that oversees the operation of nuclear power stations. This organization provides the guidelines and the frameworks on how nuclear power stations need to be operated.
Can we say that nuclear energy is a highly productive source of power?
Yes, we can say that nuclear energy is a highly productive energy source as a massive amount of energy is produced by triggering one neutron. Also, nuclear power stations are unaffected by seasonal conditions.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about nuclear fusion, energy, and much more.


Comments