Meaning of Economic System
An economic system is a mechanism with the help of which the government plans and allocates accessible services, resources, and commodities across the country. Economic systems manage elements of production, combining wealth, labour, physical resources, and business people. An economic system incorporates many companies, agencies, objects, models, and deciding procedures.
Types of Economic Systems
Capitalist economy: In a capitalist system, the products manufactured are divided among people, not according to what they want but on the basis of purchasing power, which is the ability to buy products and services. This means an individual needs to have the money with him to buy the goods and services. The low-cost housing for the underprivileged is much required but will not include demand in the market because the needy do not have the buying power to back the demand. Therefore, the commodities will not be manufactured and provided as per market forces.
Socialist economy: This economy system acknowledges the three inquiries in a different way. In a socialist society, the government determines what products are to be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of the society. It is believed that the government understands what is appropriate for the citizens of the country. Therefore, the passions of individual buyers are not given much attention. The government concludes how products are to be created and how the product should be disposed of. In principle, sharing under socialism is assumed to be based on what an individual needs and not what they can buy. A socialist system does not have a separate estate because everything is controlled by the government.
Mixed economy: Mixed systems have characteristics of both the command and the market economic system. For this purpose, the mixed economic systems are also known as dual economic systems. However, there is no sincere method to determine a mixed system. Sometimes, the word represents a market system beneath the strict administrative control in certain sections of the economy.
| Also, Explore: |
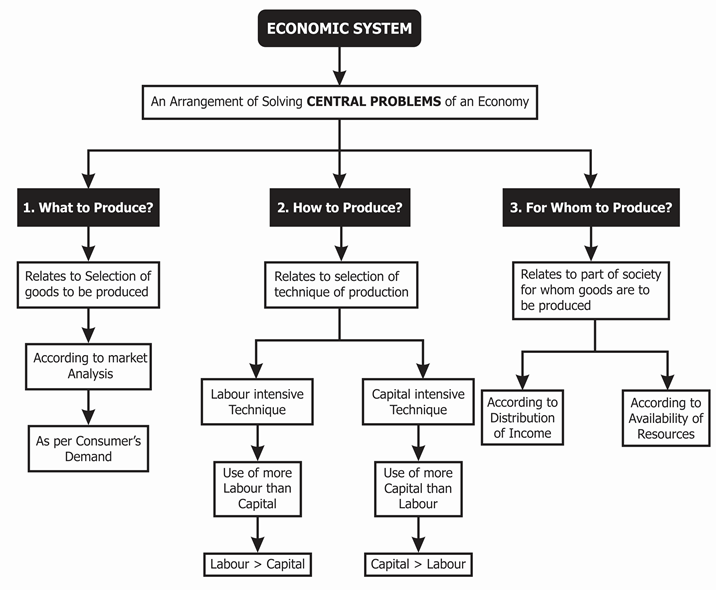
Central Problem of Economy
Economic Sector
The economic sector is divided into three economic sectors. They are as follows:
Primary sector: It is that sector which relies on the environment for any production or manufacturing. A few examples of the primary sector are mining, farming, agriculture, fishing, etc.
Secondary sector: In this sector, the raw material is transferred to a valuable product. A few examples are construction industries and manufacturing of steel, etc.
Tertiary sector: It is also known as service sector, and it includes production and exchange of services. A few examples are banking, insurance, transportation, communication, etc.
Quick Links to Explore:
Differences between Capitalist, Socialist, and Mixed Economies
| Parameters | Capitalist economy | Socialist economy | Mixed economy |
| Ownership of property | Private ownership | Public ownership | Both public and private ownerships |
| Price determination | Prices are determined by the market forces of demand and supply. | Prices are determined by the central planning authority. | Prices are determined by the central planning authority, and demand and supply. |
| Motive of production | Profit motive | Social welfare | Profit motive in the private sector and welfare motive in the public sector |
| Role of government | No role | Complete role | Full role in the public sector and limited role in the private sector |
| Competition | Exists | No competition | Exists only in the private sector |
| Distribution of income | Very unequal | Quite equal | Considerable inequalities exist |
| Multiple Choice Question: |
| Q.1. What are the central problems of an economy? |
| a. What to produce?
b. How to produce? c. For whom to produce? d. All of the above |
| Q.2. Which economic system is based on public ownership of property and social welfare? |
| a. Socialist economy
b. Capitalist economy c. Mixed economy d. None of the above |
| Q.3. Mixed economy operates with the motive of __________________. |
| a. Profit
b. Social welfare c. Both (a) and (b) d. None of the above |
| Q.4. In __________ type of economy, there is no government intervention |
| a. Socialist economy
b. Capitalist economy c. Mixed economy d. None of the above |
| Q.5. In __________ type of economy, there is no competition level. |
| a. Socialist economy
b. Capitalist economy c. Mixed economy d. None of the above |
| Answer Key |
| 1 – d, 2 – a, 3 – c, 4 – b, 5 – a |
Do you know the Advantages and Disadvantages of Organic farming?
For more data on Economics Class 11 Syllabus, Commerce notifications and sample papers for Class 11 Commerce, stay tuned to BYJU’S.

Comments